In a world where data reigns supreme, relational databases are the unsung heroes keeping everything in check. Think of them as the organized librarians of the digital age, ensuring every book (or piece of data) is shelved just right. Without these databases, chaos would reign, and finding your favorite data would be like searching for a needle in a haystack—if the haystack were on fire.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Relational Databases
Relational databases serve as foundational tools for storing, managing, and retrieving data efficiently. They utilize structured query language (SQL) to perform tasks like data querying, updating, and administration. In a relational database, information sits in tables, with each table consisting of rows and columns, much like a spreadsheet.
Data integrity and consistency remain central features. Relationships between tables foster connections through primary and foreign keys. This structure ensures that data remains organized, allowing for seamless access and manipulation.
Normalization minimizes data redundancy, promoting efficiency in storage. Each table represents a distinct entity, while the relationships establish how these entities interact. Several types of relationships exist, including one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many, catering to diverse data requirements.
Scalability addresses growing data needs. As businesses expand, relational databases can adjust to handle increased data volumes. Popular systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle Database showcase the versatility and reliability that relational databases offer.
Security measures also play a vital role. Access controls and user authentication help safeguard data from unauthorized interaction. Regular backups ensure continuity of service, preserving information integrity.
Adopting a relational database model often leads to improved data management capabilities. The clarity and structure provided by these systems enhance usability for both technical and non-technical users. Organizations leverage these databases to support analytical needs, enhance decision-making, and drive operational efficiency.
Key Features of Relational Databases
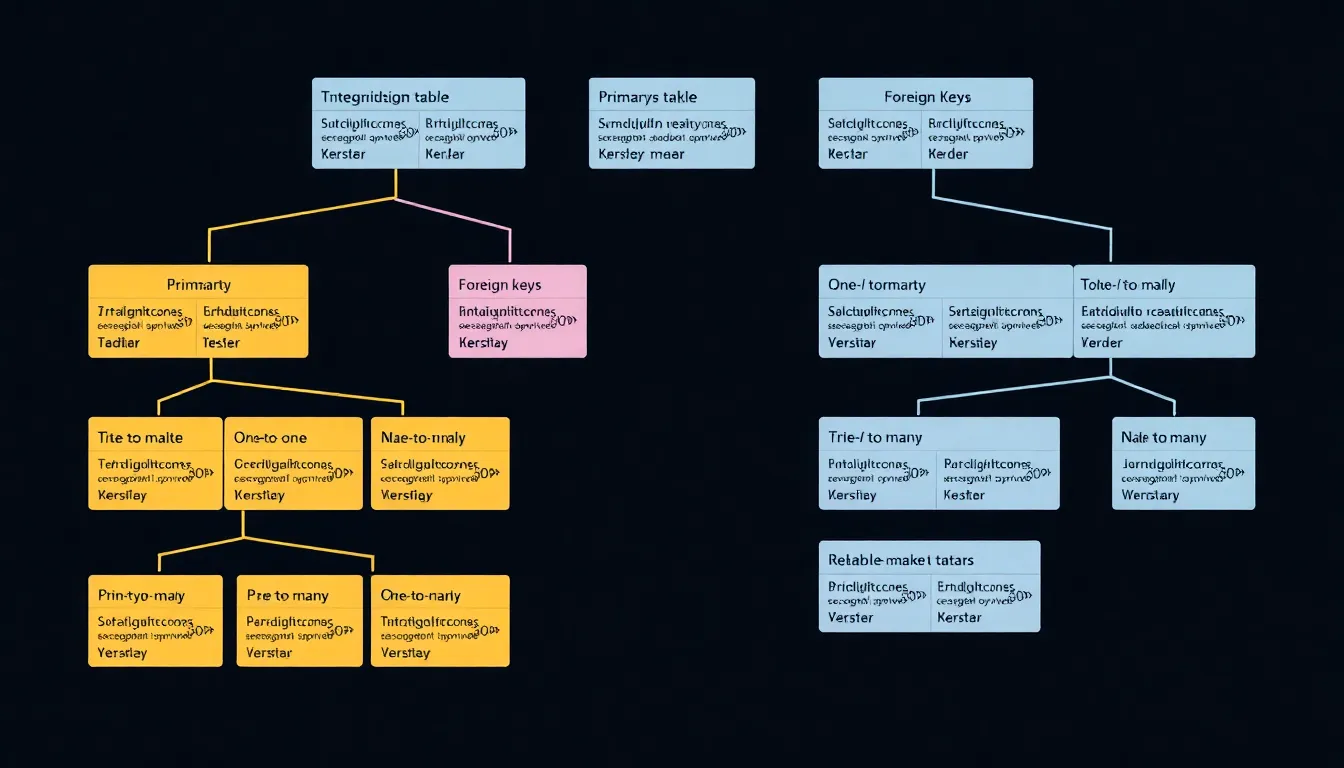
Relational databases exhibit several key features that enhance data management and retrieval. A well-defined structure supports efficient organization and access to information.
Data Structure
Tables form the foundation of relational databases. Each table consists of rows and columns, with rows representing records and columns representing attributes. Data types ensure precision and consistency, allowing fields to store specific information. Indexing boosts query performance by allowing quick access to specific rows. Normalization organizes data into distinct tables and reduces redundancy by eliminating duplicate entries. These structural principles promote data integrity, efficiency, and flexibility in storage.
Relationships Between Tables
Relationships between tables organize data meaningfully. Primary keys uniquely identify each record within a table, while foreign keys establish connections among different tables. One-to-one relationships allow a single record in one table to relate to a single record in another. In one-to-many relationships, a record from one table connects to multiple records in another, creating a more complex data structure. Many-to-many relationships allow records from two tables to connect through a junction table, enhancing data representation. These relationships foster cohesive data analysis and retrieval.
Popular Relational Database Management Systems
Relational database management systems play a pivotal role in data organization and retrieval. Several systems stand out in the industry for their reliability and performance.
Oracle
Oracle remains a leading option for enterprise-level solutions. This system supports large-scale applications and handles complex transactions effectively. Security features are robust, providing encryption and fine-grained access control. Users benefit from advanced functionalities like partitioning and clustering, improving performance. Furthermore, Oracle’s comprehensive support for various programming languages makes it adaptable for diverse development needs.
MySQL
MySQL is widely recognized for its open-source nature, appealing to developers across various sectors. Its ease of use contributes to rapid development cycles. MySQL optimizes performance with query caching and replication features, lowering response times for users. Additionally, it supports a variety of data types and storage engines, allowing for flexible data management. Community support thrives, offering extensive resources and documentation for growth and troubleshooting.
Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server excels in integration with other Microsoft products, making it a popular choice for businesses already using Microsoft’s ecosystem. This system features advanced analytics tools and a user-friendly interface. Performance tuning and optimization tools provide insights into query execution and server health. Moreover, built-in security measures like data masking and encryption ensure data protection. Additionally, its scalability accommodates growing data demands efficiently.
Understanding SQL and Its Role
Structured Query Language (SQL) plays a vital role in managing relational databases. This language provides users the ability to perform numerous tasks, such as querying, inserting, updating, and deleting data. SQL operates on tables, where data is organized in rows and columns, ensuring a clear and efficient structure.
Queries crafted in SQL allow users to retrieve specific information quickly. These requests can filter results based on various conditions, making data retrieval precise and effective. Built-in functions enhance SQL’s capabilities, allowing for calculations and aggregations directly within queries.
Data integrity remains a top priority in relational databases. SQL’s enforcement of constraints, such as primary keys and foreign keys, ensures relationships between tables remain accurate. This feature maintains the accuracy and consistency of data by preventing invalid entries.
Various SQL commands facilitate different interactions. SELECT commands retrieve data, while INSERT commands add new records. UPDATE commands modify existing entries, and DELETE commands remove specified ones. Each command serves a distinctive function, providing flexibility in database management.
Normalization further reinforces data organizations through SQL. By structuring data into related tables, redundancy diminishes, and storage becomes efficient. This structured approach enables easier updates and ensures data consistency.
Performance optimization through indexing enhances query execution speed. Indexes allow SQL to locate data rapidly, improving overall database efficiency. This functionality is crucial in environments with large data volumes.
Overall, SQL’s integration into relational databases significantly enhances data management and analysis. Its structured approach allows organizations to harness the power of their data effectively, supporting informed decision-making and operational efficiency.
Advantages of Using Relational Databases
Relational databases offer several advantages that enhance data management and retrieval. First, their structured format promotes data integrity and consistency across various applications. Each piece of data resides in a well-defined table, allowing for straightforward relationships between entities through primary and foreign keys.
Second, scalability becomes a critical feature as data volumes increase. Popular systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle Database adapt seamlessly to growing storage needs, accommodating expanding datasets effectively.
Security remains a top priority. Access controls, along with regular backups, help protect sensitive information, ensuring data is both secure and reliable. Organizations benefit from these measures, maintaining high levels of data integrity.
Furthermore, powerful tools like SQL facilitate efficient data manipulation. It allows users to execute commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, providing comprehensive control over database content. Users can retrieve precise information quickly, thanks to optimized indexing that significantly speeds up query performance.
Normalization stands out as an additional advantage, reducing data redundancy while organizing data into related tables. This approach enhances storage efficiency and supports better analysis of relationships among datasets.
Moreover, advanced functionalities present in various relational database management systems contribute to effective decision-making. Oracle excels in enterprise-level solutions with robust security features, while MySQL appeals to developers for its open-source nature. Microsoft SQL Server integrates well within ecosystems, advancing analytics and simplifying security.
Ultimately, relational databases’ structured organization, scalability, security, and powerful query capabilities lead to improved data management and informed strategic decisions for organizations.
Challenges and Limitations
Relational databases face several challenges and limitations that impact their effectiveness. Scalability presents a notable concern, particularly when applications need to manage vast amounts of data. Although relational databases handle moderate data loads well, significant increases in data volume often lead to performance degradation.
Complexity can also complicate system design. The processes required for schema design and normalization demand extensive planning and careful execution. As relationships among data grow, maintaining these schemas becomes increasingly difficult, increasing the risk of errors.
Flexibility issues arise, especially when accommodating unstructured data types. Relational databases excel with structured data but struggle with varied data forms, limiting their applicability in certain scenarios. Organizations relying on rapidly changing data may find this a significant drawback.
A lack of agility surfaces in the deployment of changes to the database schema. Modifying existing tables or adding new ones typically requires rigorous testing and sometimes downtime, which can disrupt business operations. This limitation becomes apparent when businesses require swift adaptations to their data management needs.
Cost can also be a significant factor, particularly for enterprise solutions. Licensing fees associated with commercial relational database management systems add up quickly. Open-source alternatives like MySQL offer lower costs but may lack some advanced features found in commercial counterparts.
Handling of heavy read and write operations can also become problematic. While relational databases can efficiently manage concurrent access, extreme loads may lead to bottlenecks, affecting performance and response times. Query optimization becomes essential in such situations.
Security considerations remain paramount. Despite robust security measures, vulnerabilities can still emerge, necessitating continuous monitoring and updates to safeguard against threats. Proper configurations and regular audits require resources and expertise.
Relational databases are indispensable in today’s data-centric landscape. They provide a structured approach to data management that enhances efficiency and integrity. By utilizing SQL for querying and maintaining relationships among data, these systems empower organizations to make informed decisions.
While challenges like scalability and schema complexity exist, the benefits often outweigh the drawbacks. With popular RDBMS options available, businesses can choose solutions that best fit their needs. Embracing relational databases not only streamlines data handling but also supports growth and adaptability in an ever-evolving digital world.



